Life Insurance Planning Guide
What is life insurance?
Life insurance pays out a lump sum of money called the 'death benefit' to the beneficiary, or person designated to receive the money, upon the insured's death (person insured by the policy).
As a result, the death benefit allows the beneficiary to meet any financial obligations left when the insured passes away.
How does life insurance work?
Life insurance is a unilateral contract between the policy owner and the life insurance company. Therefore, you pay a premium, and in exchange, the insurance company offers you a policy that pays a death benefit when you die.
The beneficiary can be a person(s), trust, or business. Additionally, the death benefit is paid to the beneficiary income tax-free.
What does life insurance cover?
What are the advantages of life insurance?
Life insurance can provide three main advantages:
- Death Benefit (Income Tax-Free to Beneficiary)
- Affordable protection
- Investment Value (Permanent Life Insurance)
Death Benefit
Affordable Protection
Investment Value
Why should I buy life insurance?
There are two main reasons for buying life insurance:
- Family Protection
- Business Protection
Below are the different reasons why one would purchase coverage in each situation.
Life Insurance Planning for Families:
Family Protection
If you have a family, life insurance is essential. For example, if you are the primary income earner, your family will need a way to replace your income and cover any debts when you pass away.
If you are a stay-at-home parent, your time spent parenting is a 24/7 job. Above all, your contributions to the household are essential.
Salary.com estimates the average cost to replace a stay-at-home parent would be $178,201 per year. Thus, life insurance can cover the costs of childcare and other household needs if a stay-at-home parent passes away.
Mortgage Protection
Estate Planning
Protection from Economic Life-Cycles
Divorce
Student Loans
Did your parents co-sign your loans? Will your spouse be responsible for your student loans if you pass away? It depends on the property laws of your state whether or not they will be obligated to pay your debt.
Therefore, it is crucial to consider purchasing life insurance to protect your spouse or co-signers from creditors.
Long-Term Care Planning
A long-term care rider allows you to use your death benefit to pay for long-term care. For example, the average cost of care for a private nursing home in the U.S is $7,698 per month, and in 20-years, the price will be closer to $15,383.
Therefore, imagine having to liquidate your retirement savings at an additional $15,383 per month! Long-term care planning can help offset this expense.
The Wall Street Journal's Video "Behind the Rising Cost of Long-Term Care" explains this topic.
Retirement Planning
Life Insurance Planning for Businesses:
Businesses and companies often use life insurance to protect their business. Similarly, some businesses will also use life insurance as a benefit to help recruit, retain, and retire their employees.
Below are some of the ways companies use life insurance in their planning.
Life Insurance for a Buy-Sell Agreement
Many businesses have multiple owners. Consequently, many owners ask one big question:
“What happens if one of my partners gets sick or dies prematurely?”
Life Insurance provides the liquidity (cash) needed to buy out a partner’s share in the business upon their death.
In contrast, disability insurance provides the necessary liquidity to buy out a partner due to a prolonged illness or disability.
Key-Employee Life Insurance
Life Insurance as an Employee Bonus
Life insurance policies for the benefit of the employee and their family are considered a form of employee benefit.
Therefore, these policies help businesses recruit, reward, retain, and retire top talent. Below are examples of different arrangements:
Life insurance paid by the business for the employee's family
- Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation NQDC
- Corporate Owned Life Insurance COLI
- 162-Bonus Planning 162-Bonus Planning
These topics go beyond the scope of this article. See the links above for more information about life insurance planning for businesses.
What determines the price of a life insurance policy?
- Age of Insured
- Gender
- Death Benefit Amount
- Health (Rate Class)
- Type of Policy (Term vs. Permanent)
- Riders (Additional Coverage)
Age of the Insured
The older the insured, the higher the insurance cost. In other words, the older you are, the lower your life expectancy and the higher the price will be.
So, for example, here is the most current life expectancy table from Social Security.
Gender
Insurance companies determine rates based on gender because they have assessed the risk of death based on gender alone.
So who gets the lower rates? Females. Females have a longer life expectancy which helps reduce their life insurance rates.
Death Benefit Amount
Rate Class
Healthy
Unhealthy
What are the different rate classes?
What does it mean to get "rated"?
- Preferred Best Non-tobacco (Super Healthy Discount)
- Preferred Non-tobacco (Healthy Discount)
- Standard Plus Non-tobacco (Above Average Discount)
- Standard Non-tobacco (Average Health)
- Preferred Tobacco (Healthy + Tobacco Use)
- Standard Tobacco (Average Health + Tobacco Use)
- Table Rate (Below Average Health)
Type of Policy
Riders (Additional Features)
Are life insurance rates locked in?
Term life insurance rates are locked in for the term period.
In contrast, permanent life insurance rates were initially designed to stay locked in for the contract's life.
However, since there are many different types of products and designs, we recommend you double-check the guaranteed provisions of your policy.
What are the different types of life insurance products?
Life insurance products can be broken down into two main groups:
- Term Life Insurance
- Permanent Life Insurance
There are various types of products within these groups, some being much more common than others.
What is the best kind of life insurance?
“The best kind of life insurance is the kind you have the day you die.”
Your financial goals will dictate which type of life insurance to use in your planning. In addition, your needs may change over time based on your health and financial goals, which means it’s essential to continue to review your policy.
Below is a list of the policies available in the market today.
Term Life Insurance Options
- Traditional Term Life Insurance
- Annual Renewable Term Life Insurance
- Return of Premium Term Life Insurance
Permanent Life Insurance Options
- Whole Life
- Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance
- Universal Life Insurance
- Indexed Universal Life Insurance
- Variable Universal Life Insurance
- No-Load Life Insurance
- Hybrid Life Insurance or Linked Benefit Life Insurance
We are only going to focus on the most common types of life insurance policies, which are highlighted above.
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance is the most commonly bought policy in the market. It is designed to provide coverage for a specific period of time, hence the name “term” insurance.
Furthermore, term life insurance is pure insurance like car insurance; it only pays a benefit if you die.
Term insurance is sold in 10, 15, 20, and 30-year increments. However, the most common term policies are 10-year and 20-year terms.
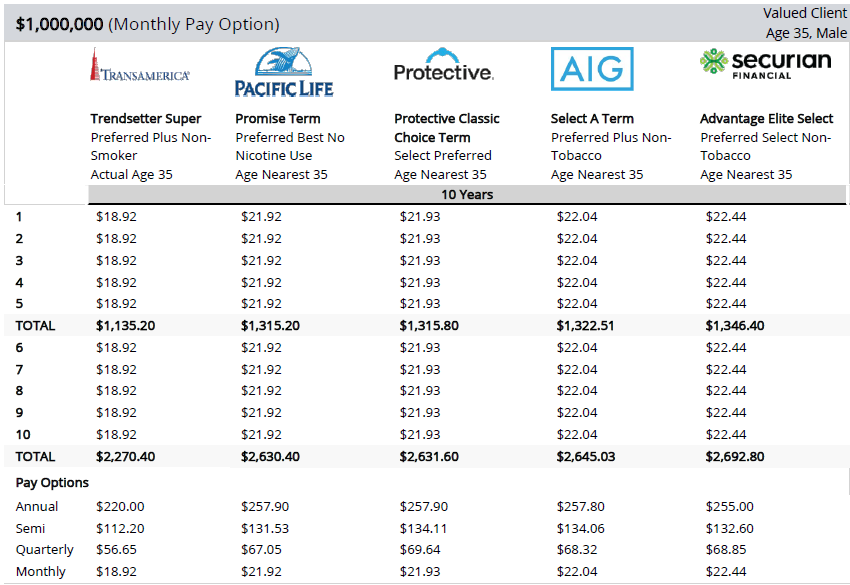
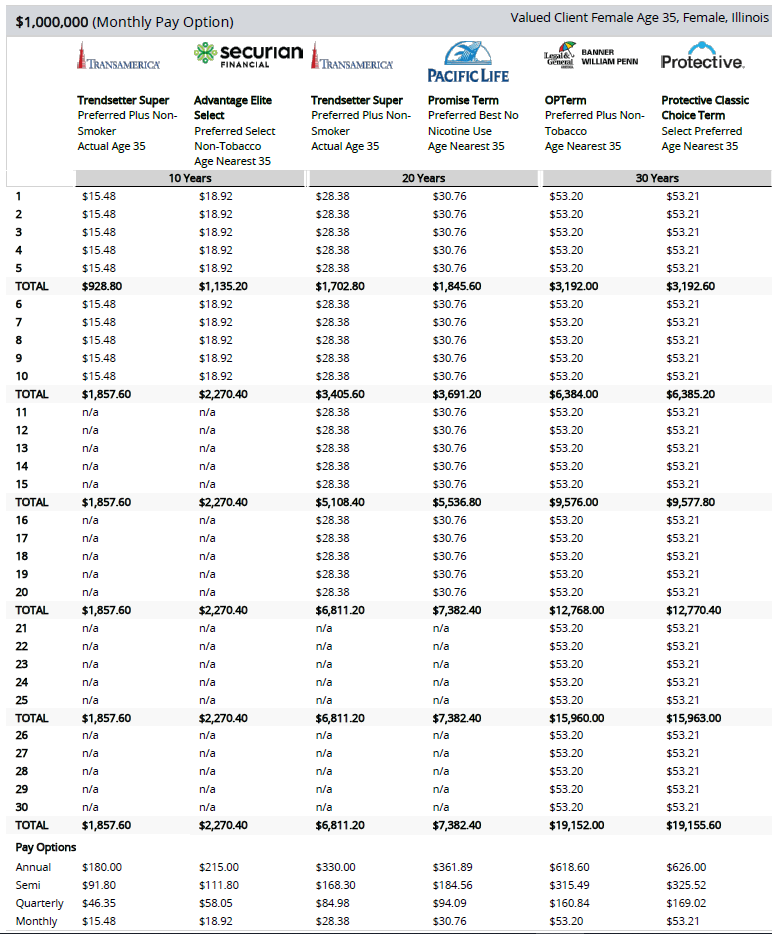
Below is an example of a term life insurance comparison quote for a healthy 35-year-old woman for $1,000,000 of coverage:
What happens at the end of a term life insurance policy?
Term life insurance rates are locked in for the given term period. When the term period ends, the policy will do one of the following things:
- The death benefit will remain the same, increasing the premium annually.
- The premium will remain the same, and the death benefit will decrease annually.
Here is why this could be important:
If you are terminally ill, you would not want your policy's death benefit to decrease.
Therefore, you'd want to be able to keep the same coverage and pay a higher premium.
Return of Premium Term Life Insurance
If you are still living and no longer desire coverage at the end of the term period, then a return of premium (ROP) term life insurance policy returns all the payments you have made.
Below is an example of a 20-year ROP term life insurance quote for a healthy 40-year-old male for a $500,000 policy.
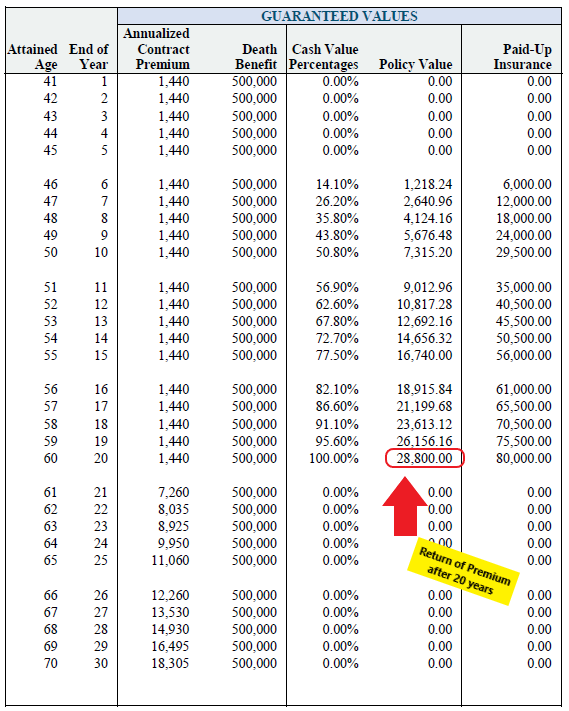
First of all, notice how in the 20th year of the policy, there is $28,800 available as a surrender value?
If the client decides to cancel the policy at 20 years, they will receive all their premium payments.
Permanent Life Insurance
There are two types of permanent life insurance: whole life and universal life. There are many variations of universal life insurance, but guaranteed universal life is the most popular.
As a result, we will mainly focus on guaranteed universal life in this article.
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance was the first life insurance product created, and it provides coverage for the entire life of the insured.
Furthermore, whole life insurance contains a savings component called the “cash value,” where savings grow tax-deferred.
Whole life insurance offers the following features:
- Lifelong Coverage
- Guaranteed Level Premiums (Price won’t change)
- Guaranteed Cash Value
- Non-Guaranteed Cash Value
How does whole life insurance work?
The premiums paid into the policy pay for the life insurance death benefit, while a portion of the premium goes into a tax-deferred savings account called the “cash value.”
The cash value earns interest and dividends, increasing the cash value over time.
Why do people buy whole life insurance?
People buy these policies to supplement their savings. This is due to the fact that the policy offers a guaranteed rate of return, called the guaranteed cash value.
The policy also has a non-guaranteed rate of return based on the insurance company's performance.
Below is an example illustration of a Whole Life policy for $100,000 in coverage for a healthy man, age 60:
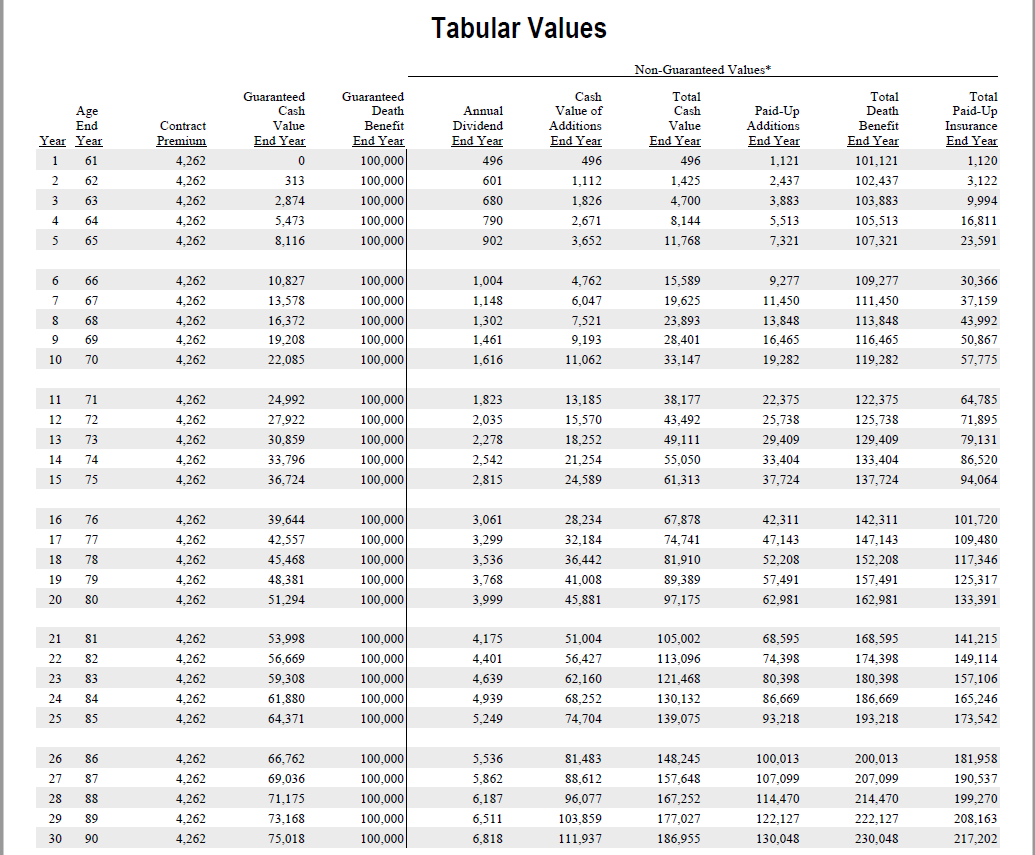
Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL)
Guaranteed universal life insurance was created to compete against whole life insurance. The goal, therefore, is to provide permanent life insurance that lasts the insured’s entire life at a lower cost.
It is usually about half the cost of whole life insurance.
The reason GUL is less expensive than whole life is that it grows little to no cash value over time.
Its primary purpose is the death benefit.
GUL offers the following features:
- Lifelong Coverage
- Level Guaranteed Premiums (Price won’t change)
How does a GUL policy work?
When the client pays the required premium and doesn’t take any loans or withdrawals from the cash value, the policy will pay the death benefit when the insured passes away.
Below is an example illustration of a Guaranteed Universal Life policy for $100,000 in coverage for a healthy man, age 60:
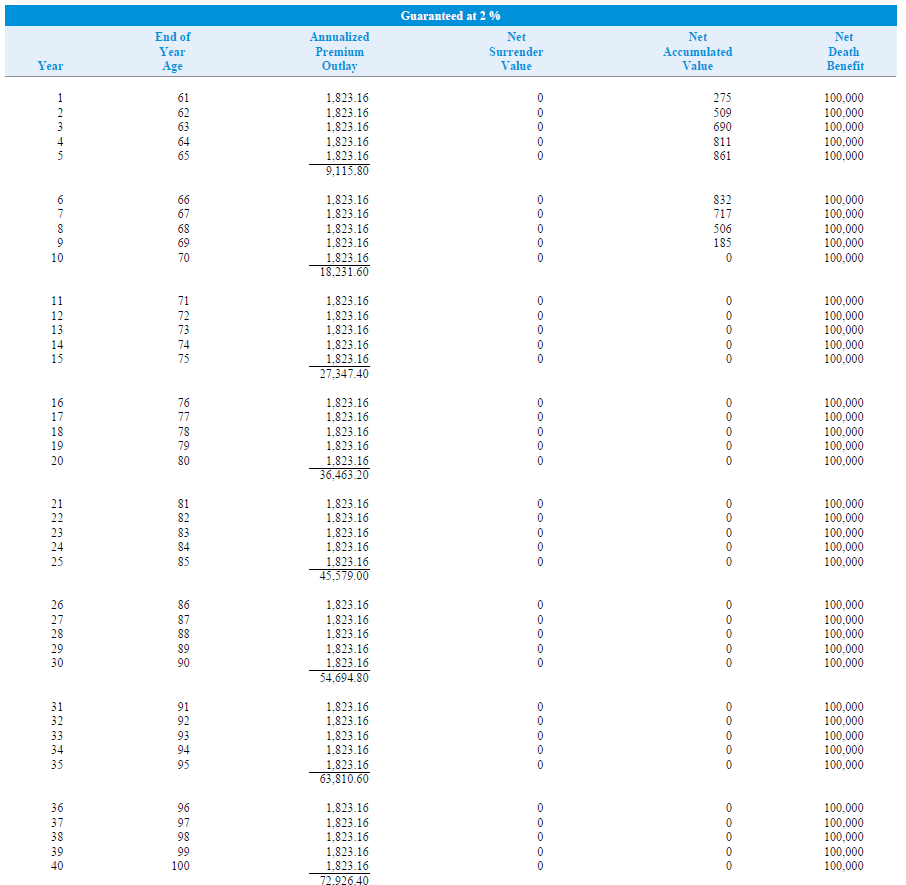
Whole Life vs. Guaranteed Universal Life
After analysis, both policies offer guaranteed death benefits, premiums, and a guaranteed premium payment structure.
The main difference between whole life and guaranteed universal life is that a GUL policy will build little to no cash value.
Because of this, all other things equal, the GUL policy is about half the cost of a Whole Life Policy.
What factors affect the pricing of life insurance?
Underwriting is the most crucial part of obtaining the lowest price on your life insurance. Your goal, therefore, is to find the lowest-priced option and find an insurance company that will offer you those rates. Indeed, this is where an experienced life insurance expert will come in handy.
Insurance carriers look at your current and past health, tobacco use, family health history, lifestyle, and avocations.
Health of Client
Tobacco Use
Many insurance companies don’t like tobacco use, especially cigarettes. As a result, cigarette users typically pay rates three to fives times more than non-tobacco users.
In contrast, some insurance carriers may offer non-tobacco pricing for chewing tobacco or cigar use.
Prescription History
Every carrier, or insurance company, will review your prescription history from the past five to ten years.
If they find conflicting information, they will request a copy of your medical history to cross-examine it.
Family Health History
Driving History
If you have more than three moving violations in five years or a DUI in the past ten years, you're not going to qualify for the best rates.
So even though you may be healthy, companies will consider you a higher risk.
Avocations of Insured (Lifestyle)
Do you fly planes? Rock Climb? Race Cars? Scuba Dive? Heli-Ski? Spelunk?
For those reasons, you may be a little tougher to underwrite depending on how often you participate in these activities and the level of extremity.
How do I save money on life insurance?
You may think there is a secret company, but there isn't. The best way to get the best price on your life insurance is to obtain the best underwriting offer.
The difference between company A and Company B in the same rate class is $.50 a month, or less than 1%.
The difference between the best rate vs. the second-best rate is 25%.
How to obtain the lowest life insurance rates and best underwriting offer:
- Work with a life insurance expert.
- Review multiple quotes. (It’s free to review quotes.)
- Shop your case with underwriters.
What should I look for in a life insurance broker?
You're ready to find a life insurance professional now that you have done your research.
It’s important to remember that there is no “best” professional to work with. Instead, we have laid out what to look for in a life insurance expert.
Below are the three principal traits to look for in a professional:
- Trust
- Experience
- Education
Trust
Do you trust they are doing what is in your best interest? Here are some things that can help you build trust.
- Are they able to work with multiple insurance companies?
- Do they have a designation like a CFP®, CLU®, ChFC®, or MSFS?
- Is there a fiduciary responsibility? Fiduciary vs. Suitability
Experience
Here are some ways to figure out if they are experienced:
- Do they know how to determine how much coverage you need?
- Do they know how to obtain the best rate through underwriting?
- Can they explain how they will help you obtain the best rate?
Education
Designations are a set of letters after a professional’s name, which signifies that they have completed additional education to be designated a professional by that organization.
Furthermore, some designations are harder to obtain than others. For instance, some require a one-day seminar, while others require completion of 6 courses plus a comprehensive case analysis followed by a cumulative 6-hour examination (CFP®)
As a result, we recommend the following designations for life insurance planning: CFP®, CLU®, ChFC®, or MSFS.
Do brokers need a Securities Registration to sell life insurance?
A securities registration is not necessary to sell life insurance, but it is required to present and sell variable life insurance.
As a result, an un-registered life insurance broker can’t present or sell these products. Therefore, if you are interested in learning about these options, make sure your broker is a registered representative.
Which advisor is the best for life insurance planning?
The best advisor is the one with life insurance expertise, the ability to shop with different insurance carriers, understands life insurance underwriting, and makes you feel the most comfortable with the process.
Above all, if you can trust your advisor, that’s the best one to work with.
What type of professionals advises on life insurance planning?
- Captive Life Insurance Agent
- Career Agents
- Independent Life Insurance Broker
- Online Life Insurance
- Fee-Based or Fee + Commission Financial Advisor
- Fee-Only Financial Advisor
What do you need to sell life insurance?
Your broker or agent needs to pass state testing and hold a license in the states they conduct business.
In addition, if they want to sell variable life insurance, they need to be securities registered with Series 6 and 65 & 63.
Captive Life Insurance Agent
Captive agents can only sell their parent company's products. Hence they are "captive." However, they cannot provide outside options from other companies.
For example, some captive insurance carriers may allow other options to be sold only if the client is declined a policy from the parent company first.
Career Agents
Career agents work for a parent company but can sell products from other insurance companies.
Furthermore, many career agents work for mutual insurance companies which sell many of the whole life policies available on the market.
Independent Life Insurance Broker
Independent brokers work with multiple insurance companies. Sometimes they may also sell other types of insurance like homeowners, auto, business, health, and other lines of business.
Additionally, brokers can be individuals or large agencies like Aon, Hub, Gallagher, Mash, or local brokers listed on Trusted Choice.
Large Brokers: Marsh, Aon, Willis, Gallagher, HUB
Smaller Brokers: Trusted Choice
Carriers: Lincoln Financial, Prudential, AIG, Principal, Legal & General, Grange, Erie
Online Life Insurance Brokers
Fee-Based Financial Advisor or Fee + Commission Financial Advisor
Not to be confused with "fee-only," these advisors may charge a fee and receive commissions.
Fee-based advisors can earn income in the following ways:
- Assets Under Management (Percent of Assets Managed)
- Fee for Service
- Commissions on Stock, Mutual Fund, or Bond Trades
- Commissions on Insurance Sales
Fee-Only Financial Advisor
Fee-only financial advisors earn their income by charging a fee for service or a fee based on assets under management (AUM).
Because of this, they cannot earn a commission on a life insurance policy.
As a result, they still need to partner with an insurance broker to place any life insurance business and cannot receive any form of compensation in return.
Examples Fee-Only Advisors: Fisher Investments, Hall Capital Partners, Moneta Group
Examples Local: NAPFA Organization
How to determine how much life insurance you need?
There are three ways to determine how much life insurance you need1:
- Multiple of Income Approach
- Financial Needs Analysis Approach
- Capital Needs Analysis Approach
The most common way to determine your need is the Multiple Income Approach or the Capital Needs Analysis, but that doesn’t make them the best.
There are two concepts to understand:
- Replacement Income– The amount of money you are replacing on an annual basis.
- Replacement Period– The length of time during which you want to replace that stream of income.
Multiple of Income Approach (MIA)
How it works:
- Replacement Income = $75,000 (Income)
- Replacement Period = 5 years
- Death Benefit = $375,000 (5 years x $75,000)
Issues:
This option isn't very accurate because it doesn't account for investing the funds. It also doesn't consider any other assets or liabilities you may need to consider.
The next two options do a better job of assessing your actual need.
Financial Needs Analysis Approach (FNA)
This approach accounts for your entire financial picture by including debt, expenses, college planning, and assets.
When determining your death benefit, consider how much money your family would need on the day after your death to invest, grow and account for your family's expenses for the rest of their lives.
How it works:
- Replacement Income = $75,000 (Income 20 Years after death)
- Replacement Period = 20 Years (Spouse turns 65) Assumed IRR = 5% (Assumption)
- Death Benefit = $934,666 (will return $75K annually for 20 years)
The financial needs approach and the capital needs approach differ in that , with the financial needs approach, none of the original death benefit is left at the end of the replacement period.
Capital Needs Approach (CNA)
How it works:
- Replacement Income = $75,000 (Yearly Income Lifetime)
- Replacement Period = Lifetime Assumed IRR = 5% (Assumption)
- Death Benefit = $1,500,000 ($75,000 annually for life)
Financial Needs Approach vs. Capital Needs Approach?
The financial needs approach will generate a lower death benefit amount, thereby reducing the cost of insurance. In contrast, the capital needs approach will provide lifetime income and the death benefit will be higher.
Which formula you choose depends on your goals. Additionally, some people prefer an amount in the middle.
How much life insurance do older people need?
How much life insurance do younger people need?
Which type of life insurance policy should I buy?
You're 35, and you plan on retiring at age 65; you, therefore, may only need coverage for 30 years.
Additionally, if you want to keep coverage past retirement, it may be good to purchase a permanent policy now.
This is because you are healthy, younger, and have time to build cash value (equity) inside the policy right now.
How much life insurance do you want to keep past retirement?
Life insurance past retirement can help you with the following financial goals:
- Estate Taxes
- Liquidity at Death
- Protection from Economic Life-cycles
- Long-Term Care Funding
Depending on your financial goals, you may want to consider a permanent life insurance plan.
What are the different ways life insurance is underwritten?
There are four ways life insurance policies are underwritten.
- Traditional Underwriting
- Accelerated Underwriting
- Simplified Issue Underwriting
- Guaranteed Issued Underwriting
Since traditional underwriting is the most comprehensive and commonly used underwriting option, we will focus on how this process works.
How does the life insurance underwriting and application process work?
Here are the steps to apply for and obtain a traditional life insurance policy.
- Review the Coverage
- Submit an Underwriting Questionnaire
- Apply with Best Offer
- Complete Underwriting
- Obtain Medical History
- Place Coverage In-Force
1. Review the Coverage
First of all, you’ll want to determine your death benefit and type of life insurance policy. Then, you’ll narrow down which insurance carriers to work with.
COMPARE: Different Accelerated Underwriting Life Insurance Options
2. Submit an Underwriting Questionnaire
Why is an underwriting questionnaire a great way to shop for life insurance?
Your questionnaire will be sent out to various insurance companies without any of your identifying information.
In contrast, if you were to submit a formal application and receive a decline, it would be recorded in the MIB, making it difficult to obtain a better rate somewhere else.
What is the MIB?
3. Apply with Best Offer
4. Complete Underwriting
Background Check
- Motor Vehicle Report
- Prescription History Record
- MIB Record
- Credit Report
Exam:
Not every carrier requires an exam. It depends on the results from your background check, age, and the amount you are applying for.
If an exam is required, below is what they most commonly request.
- Blood Analysis
- Urinalysis
- Height and Weight
- Blood Pressure Reading
Don’t want to complete an exam?
READ: How you can get an exam free life insurance policy during COVID-19:
5. Obtain Medical History
Depending on the information disclosed during the phone interview, background check, or exam, the carrier may then want to review copies of your medical history.
Additionally, if you have any conflicting information in your background check, the carrier will request your medical history.
6. Place Coverage In-Force
Once the underwriter has reviewed all the information, they will make an offer. You could receive the “tentative” offer, a better offer, a worse offer, or be declined.
If there is a better option available, you’ll then be able to reapply with a new carrier.
Placing the life insurance policy in-force
Before you place the policy in-force, you can adjust the death benefit and type of policy.
Coverage is only in-force when the carrier has received the first payment.
What other features can I add to a life insurance policy?
Riders allow you to add additional coverages or provisions to your policy, thus offering more benefits for different needs.
Below are examples of the most common riders:
Accidental Death Rider
Child Rider
Long-Term Care Rider
Waiver of Premium or Disability Rider
What is a life insurance policy review?
A policy review is a process of reviewing the following components of your life insurance policy:
- Death Benefit Amount
- Coverage Length
- Conversion Option (Term Only)
- Performance (Permanent Only)
- Policy Features
Reviewing a term life insurance policy is simple. You want to determine the following:
- Death Benefit (Do you need more?)
- Term Length (Do you need it to last longer?)
- Conversion Option (When does it expire? Do I need to convert?)
If you find yourself with a higher mortgage, more kids, higher debt, or higher income, it may be time to increase your coverage.
What is a "conversion option" on a life insurance policy?
Most term policies offer a conversion feature, or rather, the ability to exchange your term policy for a permanent policy without proof of insurability.
However, many insurance companies restrict when you can convert a policy. As a best practice, it’s a good idea to know when those limitations will apply.
Performance Review
If you own a permanent life insurance policy, you should be reviewing your policy's performance.
Just as you review your investments and portfolio, you want to ensure your policy is performing as expected.
Above all, this allows you to make any policy changes before major issues arise.
Policy Features
Even insurance companies come out with new features, and one of the most popular features available today is a life insurance policy that contains a Long-Term Care Rider.
While these riders were not available 10 years ago, they have become popular today. This is probably because this rider allows the insured to access the death benefit before death to pay for long-term care costs.
How often do you conduct a life insurance policy review?
FAQ’s about your life insurance policy:
What is the contestability period of a life insurance policy?
Every life insurance policy has a two-year contestability period. In other words, if the insured passes away within two years, the insurance company has the option to contest the policy and investigate to determine if any fraud has been committed.
Conversely, the carrier simply pays the claim if the client passes away after the two-year contestability period.
Does the life insurance company still pay the death benefit in the case of suicide?
If the insured purchases a policy and commits suicide within the first two years, the insurance company will not pay out the death benefit and will return all premiums paid.
In contrast, if the insured commits suicide after the two-year contestability period, the carrier must pay the death benefit.
National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 1-800-273-8255
What if I lie on my life insurance application?
We recommend that you don't lie. You don't want to purchase a policy, and your spouse to find out it isn't going to pay because you lied.
Your best bet is to review your concerns with your broker to determine your coverage options.
What if I lie on my life insurance application during underwriting?
If you lie on your life insurance application, the insurance company will try to uncover any other inconsistencies and possibly decline your case.
As a result, this may make it difficult to obtain coverage from another insurance company.
What if I lie on my life insurance application and die during the Two-Year Contestability Period?
If you lie or fail to disclose information on your life insurance application, and you pass away during the two-year contestability period, the carrier will contest the claim.
For example, if you do not disclose that you have a history of recorded drug use (hospitalizations or criminal activity), and the underwriter fails to discover it during the underwriting process, the carrier will have the ability to contest the claim.
For that reason, the carrier may not pay out the death benefit when you pass away.
What if I lie on my life insurance application and die after the Two-Year Contestability Period?
In contrast, if you lie or fail to disclose information on your life insurance application and pass away after the 2-year contestability period, the carrier must pay out the claim.
Using the example above, if that same person passed away three years later, after not disclosing their drug use history, the carrier could not contest the claim.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we hope that The Definitive Guide to Life Insurance Planning gives you a solid understanding of all aspects of life insurance planning.
If there are any topics you think we missed, please let us know by sending us an email, and we'll add them to the guide.
Working with Jerry C. Thomas, CFP®
If you need assistance with your insurance planning, we are a full-service agency specializing in helping you find the best life insurance at the lowest prices to meet your financial goals.
Our goal is to provide life insurance planning using a fiduciary model: we offer what is in the clients' best interest at all times.

